epiglottis x ray
Obliteration of the vallecula vallecula sign may be seen figure above white arrow. Chest X-rays X-ray Treatment Treatment of epiglottitis involves first making sure you or your child can breathe and then treating any identified infection.
References 21 public playlist include this case.

. An ultrasound may be helpful if specific changes are present but its use as of 2018 is in the early stages of study. When seen on a lateral neck radiograph an omega epiglottis can appear prominent mimicking the epiglottic thickening seen in epiglottitis 14 and all causes of epiglottic enlargement in general. It represents the so-called thumb sign.
There is also reversal of the normal lordotic curve in the cervical spine and slight dilatation of the hypopharynx. We report the MRI findings in an adult with epiglottitis. Because of her risk factors for malignancy CT scan was requested and revealed only benign features.
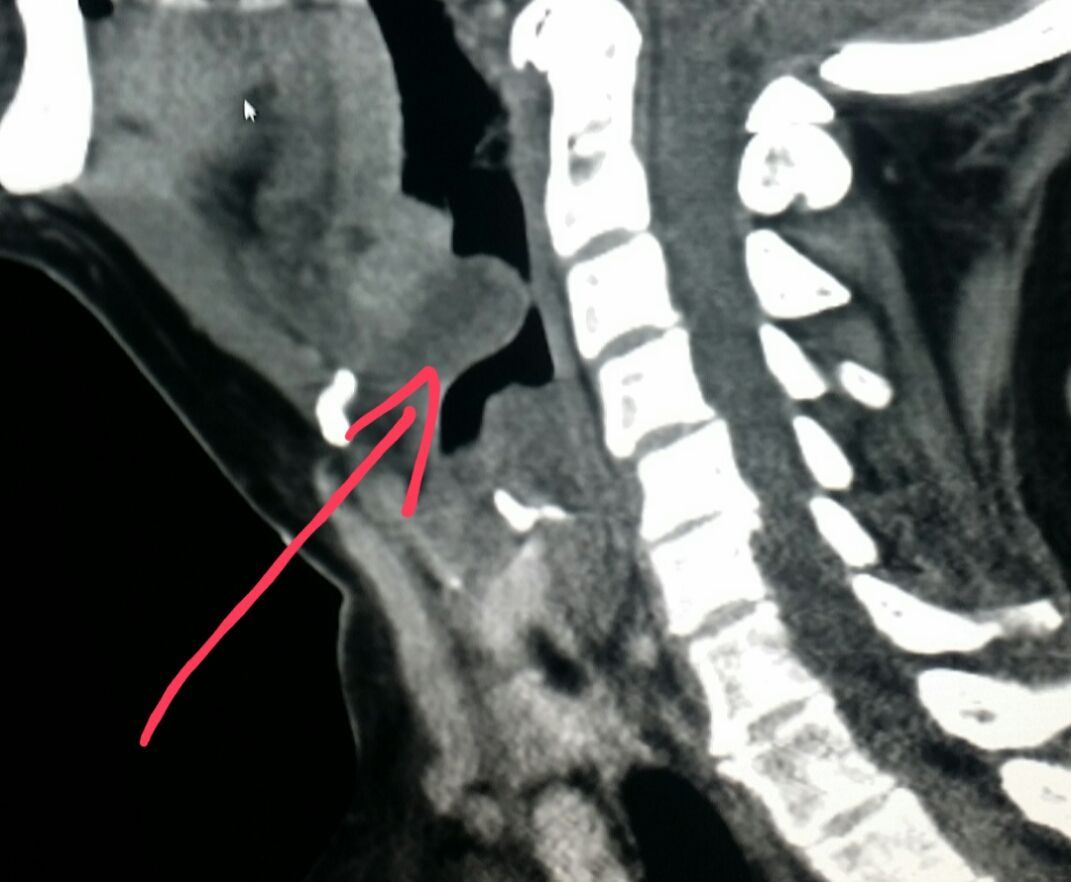
Management of this life-threatening condition requires imaging only when the diagnosis is uncertain or when an abscess or other complication is suspected. Epiglottitis is a systemic infection that results in. Lateral radiograph of the neck demonstrates and enlarged epiglottis red arrow and thickening of the aryepiglottic folds yellow arrow.
It represents the so-called thumb sign. References 24 public playlists include this case Promoted articles advertising. Epiglottitis is a systemic disease that involves the supraglottis especially the epiglottis.
There is no reported gender predilection. Helping you breathe The first priority in treating epiglottitis is ensuring that you or your child is receiving enough air. Based on this two-part study it is our conclusion that the lateral neck and chest x-ray may be unreliable and inaccurate in the diagnosis of croup and epiglottitis.
Epiglottitis is inflammation and swelling of the epiglottis. A normal X-ray however does not exclude the diagnosis. On lateral soft tissue X-ray of the neck the thumbprint sign a finding that suggests the diagnosis of epiglottitis is seen.
The mask delivers oxygen to the lungs. This shows as a hemispherical mass at the base of the tongue replacing the normal slender coma shape of the epiglottis. A neck or chest X-ray is ordered to examine the region and the epiglottis.
88 sensitive so a negative X-ray doesnt exclude epiglottitis. We present a 65-year-old female with an incidental 1 cm exophytic pedunculated papillomatous lesion on the laryngeal surface of the epiglottis discovered upon endoscopic evaluation for dyspepsia and heartburn. This disease usually occurs in children between the ages of 2 and 4 although recent reports suggest that its incidence is increasing in patients 2 years of age.
The epiglottis is a flap of tissue that sits beneath the tongue at the back of the throat. Caution and good clinical judgement should be utilized when interpreting these x-rays. MeSH terms Adult Child.
On lateral C-spine X-ray the thumbprint sign describes a swollen enlarged epiglottis. Throat examination A doctor uses a flexible fiber-optic tube comprising a light that looks down the throat to find out the cause for the symptoms. Thus this anatomic variant represents a potential pitfall in evaluating neck radiographs.
Its main function is to close over the windpipe trachea while youre eating to. References Promoted articles advertising. Appearance of the epiglottis during upper airway sonography J Ultrasound Med.
On CT imaging the Halloween sign describes an epiglottis of normal thickness. There was thickening of the epiglottis and left aryepiglottic fold. The X-ray may show something like a thumbprint within the neck and this is an indication that the epiglottis is enlarged.
Lateral x-ray of the neck of the a child presenting with clinical epiglottitis demonstrates swelling of the epiglottis which projects as a rounded soft tissue structure into the hypopharynx. The thumbprint sign is a manifestation of swollen and edematous epiglottis. Appearance of the epiglottis during upper airway sonography.
Of interest 24 had readings consistent with possible epiglottitis. Gross anatomy The epiglottis projects posterosuperiorly from its stem-like base which is attached to the thyroid cartilage. Lateral x-ray of the neck of the a child presenting with clinical epiglottitis demonstrates swelling of the epiglottis which projects as a rounded soft tissue structure into the hypopharynx.
The epiglottis is a single midline leaf-shaped fibrocartilaginous structure that forms part of the supraglottic larynx and defines the division of the hypopharynx from the larynx. Lateral neck x-ray Findings Swollen epiglottis may be seen as a thumb sign normally epiglottis profile should look like a finger. Its often caused by an infection but can also sometimes happen as a result of a throat injury.

Inspiratory Stridor And Diaphoresis Spell Emergency

Epiglottis Nursing Flashcards Nurse Rock Flashcards

What Is Epiglottis Definition Function Problems Pain Epiglottitis Infection Updated In 2022

Pin By Shanto Urutyan On Anatomy In 2022 Radiology Medical Radiography

Epiglottitis Radiology Imaging Medical Imaging Basic Anatomy And Physiology

Indications Of Thumbprint Sign In Chest Abdominal X Ray

Normal Lateral Neck Radiograph Radiology Student Medical Knowledge Radiology Imaging











Comments
Post a Comment